Borrowing cost IAS 23,benchmark treatment of borrowing cost and alternate treatment of borrowing cost with exercises
IAS 23 Borrowing cost
IAS 23 (Borrowing cost) deals with the cost (interest/financial charges) of such borrowings that
are incurred from purchase, acquisition or construction/production of assets.
Two very important terminologies of this standard need explanation, before going into the further details.
1) Borrowing Costs:
These are interest and other costs incurred by an entity in connection with the borrowing of funds.
Examples of Borrowing Costs:
(a) Interest on bank overdrafts and short-term and future borrowings;
(b) Amortization of discounts and premiums relating to borrowings;
(c) Amortization of ancillary costs incurred in connection with the arrangement of borrowings (e.g. processing fee, lawyer’s consultation etc.);
(d) finance charges in respect of finance leases recognized in accordance with IAS 17, Leases; and
(e) Exchange difference comes from foreign currency borrowings to the extent that they are considered an adjustment to interest cost.
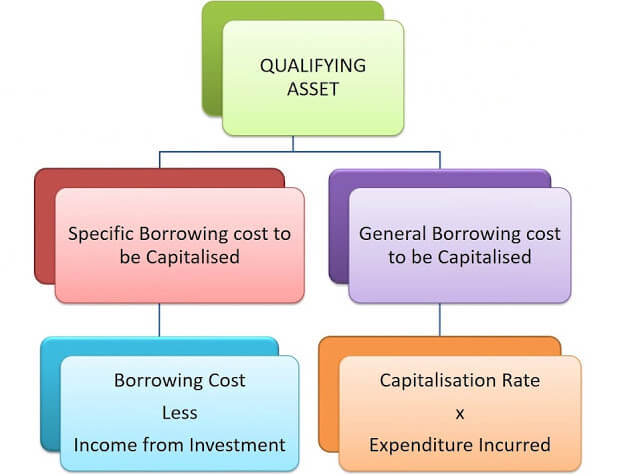
2) A qualifying asset:
It is an asset that necessarily takes a considerable period of your time to urge ready for its intended use or sale.
Examples of Qualifying Assets:
a) Manufacturing plants
b) Power generation facilities
c) Investment properties
d) Those inventories which are routinely manufactured or produced in large quantities on a repetitive basis and assets ready for their intended use or sale when acquired are not qualifying assets.
Question 1
Identify which of the followings are qualifying assets:(a) Power plant being in the process of manufacturing.
(b) Inventories routinely manufactured;
(c) Asset ready for use;
(d) Inventories requiring a substantial period for manufacturing.
(e) Special order for a special inventory which will be manufactured in 5 months.
Solution 1
(a) Qualifying Asset;(b) Not Qualifying Asset;
(c) Not Qualifying Asset;
(d) Qualifying Asset;
(e) Qualifying Asset.
Accounting treatment for borrowing costs
There are two methods involve in the accounting treatment of borrowing cost.
- Benchmark treatment
- Alternate treatment
1) Benchmark Treatment:
Recognition:
Under the benchmark treatment borrowing costs are recognized as an expense within the period during which they're incurred no matter how the borrowings are applied.
Disclosure:
The financial statements shall disclose the accounting policies adopted for borrowing costs (e.g. Interest, markup, profit and other charges on borrowings are charged to income).
2) Allowed Alternate Treatment:
Recognition:
Borrowing costs shall be recognized as an expense within the period during which they're incurred, except to the extent that borrowing costs that are directly due to the acquisition, construction and production of a qualifying asset shall be capitalized as part of the cost of that asset.
Borrowing costs eligible for capitalization:
The borrowing costs that are directly due to the acquisition, construction or production of a qualifying asset are those borrowing costs that might are avoided if the expenditure on the qualifying asset had not been made. When an entity borrows funds specifically for the aim of obtaining a specific qualifying asset, the borrowing costs that directly relate thereto qualifying asset are often readily identified.
Exercises
Question 2
Mega Limited is engaged within the production of power generation plants, which is to be used by the company. The company borrows Rs.20, 000,000 @ 10% for construction of the plant. The company wants to adopt the policy for accounting treatment of interest expense on such borrowings. What options are available to the corporate under IAS-23, Borrowing Costs?
Solution 2
Benchmark Treatment
Interest expense is recognized as an expense in the period in which it is incurred. Therefore, the corporate under benchmark treatment should recognize the interest of Rs. 2,000,000 as an expense.
Allowed Alternative Treatment
Under allowed alternative treatment, the expense of Rs. 2,000,000 shall be capitalized in the cost of the asset.Specific Borrowings
Where funds are borrowed specifically for a qualifying asset, the quantity of borrowing cost (less temporary investment income if any) shall be capitalized as a price of such asset.
Temporary Investment Income
When all of the borrowed funds are not utilized at once for acquisition, development or construction of qualifying asset, the un utilized amount of the borrowed fund is invested temporarily(for a little time period) in some securities. The return on such investments is known as temporary investment income.
Question 3
Swan Limited borrowed a loan from bank @ 12% per annum amounting to Rs.1,000,000 for the construction of power generation facilities of the company. The loan was received on January 01 and utilized Rs. 300,000 on Qualifying Asset. On January 01, the corporate deposited the remaining amount during a bank yielding interest @ 6%. Whole of the quantity is withdrawn and paid to contractor on March 01. The company returned back the loan to bank after 9 months i.e. on October 01. You are required to calculate the amount of borrowing cost eligible for capitalization.
Hint:
Borrowing period 9 monthsInvestment period 2 months
Solution 3
Particulars Rs.Interest paid to bank 1,000,000 x 12% x 9/12 90,000
Less: Interest income 700,000 x 6% x 2/12 (7,000)
Borrowing cost eligible for capitalization 83,000
Capital expenditure (Rs. 1,000,000 + 83,000) 1,083,000
General Borrowings:
The amount to be capitalized shall be computed on the basis of capitalization rate, which shall be the weighted average of the borrowing costs applicable to the outstanding borrowing during the period.
This rate when charged on the expenditure incurred on Qualifying Asset on a time basis gives the amount of borrowing cost to be capitalized. The capitalization should not exceed the amount of borrowing costs actually incurred.
Question 4
MCQ (Private) Limited has the following loans outstanding as at December 31, 2006.Particulars Rs.
Loan – 1 @ 6% (Due since starting date) 300,000
Loan – 2 @ 8% (Taken on 1 April, 2006) 200,000
Loan – 3 @ 9% (Taken on 1 July, 2006) 150,000
The company paid following amounts on construction of an asset.
January 31, 2006 70,000
April 1, 2006 80,000
December 1, 2006 10,000
Calculate
(i) Capitalization Rate
(ii) Borrowing cost eligible for capitalization.
Solution 4
(i) Capitalization rate 7% (W-1)(ii) cost eligible for capitalization Rs.9, 136 (W-2)
Working:
(W-1) Capitalization Rate.
Loan Amount (Rs) W Avg. Rate (Rs) Interest (Rs)
Loan – 1 300,000 300,000 6% 18,000
Loan – 2 200,000 (9/12)150,000 8% 12,000
Loan – 3 150,000 (6/12) 75,000 9% 6,750
Total 650,000 525,000 36,750
Capitalization rate =Total Interest / Weighted Average Loan x 100
=36,750 / 525,000 x 100
Capitalization rate = 7%
(W-2) Borrowing cost eligible for capitalization.
Expenditure Incurred on Rate Period Capitalization (Rs)
70,000 January 31, 2005 7% 11/12 4,492
80,000 April 01, 2005 7% 9/12 4,200
10,000 December 01, 2005 7% 1/12 58
160,000 8,750
Particulars Rupees
Total borrowing cost 36,750
Borrowing cost eligible for capitalization (8,750)
Borrowing cost chargeable as expense 28,000
Capital Expenditure Rs.
Incurred cost 160,000
Borrowing cost eligible for capitalization 8,750
Total 168,750
Question 5
MCQ (Private) Limited has the following loans outstanding as at December 31, 2006.Particulars Rs.
Loan – 1 @ 6% (Due since starting date) 300,000
Loan – 2 @ 8% (Due since starting date) 200,000
Loan – 3 @ 9% (Due since starting date) 150,000
The company paid following amounts on construction of an asset.
January 31, 2006 70,000
April 1, 2006 80,000
December 1, 2006 10,000
Calculate
(i) Capitalization Rate
(ii) Borrowing cost eligible for capitalization.
Solution 5
(i) Capitalization rate 7.31% (W-1)(ii) cost eligible for capitalization Rs.9, 136 (W-2)
Working:
(W-1) Loan Amount (Rs) Rate Interest (Rs)
Loan – 1 300,000 6% 18,000
Loan – 2 200,000 8% 16,000
Loan – 3 150,000 9% 13,500
650,000 47,500
Capitalization rate =Total Interest / Total Loan x 100
=47,500 / 650,000 x 100
Capitalization rate = 7.31%
(W-2) Borrowing cost eligible for capitalization.
Expenditure (Rs) Incurred on Rate Period Capitalization (Rs)
70,000 January 31, 2006 7.31% 11/12 4,689
80,000 April 1, 2006 7.31% 9/12 4,386
10,000 December 1, 2006 7.31% 1/12 61
160,000 9,136
Particulars Rupees
Total borrowing cost 47,500
Borrowing cost eligible for capitalization (9,136)
Borrowing cost chargeable as expense 38,364
Capital Expenditure
Incurred cost 160,000
Borrowing cost eligible for capitalization 9,136
Total 169,136
Question 6
Sublime Sports Limited is currently manufacturing its power plants. Up-to December 31, 2003, the company has incurred costs totaling Rs.500, 000 on production of one of its plant.The following loans are outstanding:
Particulars Rs.
Loan from MCB @ 9% 500,000
Loan from HBL @ 10% 625,000
Loan from UBL @ 11% 375,000
Loan from HBL was taken on July 1, 20x3 other loan were brought forward from previous year.
Expenditure on plant incurred as follows:
May 31, 2003 300,000
July 31, 2003 200,000
You are required to calculate:
(a) Capitalization rate of the company;
(b) Total cost to be capitalized for the year 2003.
Solution 6
(a) Capitalization rate 9.8947% (W-1)(b) Total borrowing cost eligible for capitalization Rs. 25,562 (W-2)
Workings:
(W-1) Principal W Avg.Loan (Rs) Rate Interest (Rs)
Loan from MCB 500,000 12/12 500,000 9% 45,000
Loan from HBL 625,000 6/12 312,500 10% 31,250
Loan from UBL 375,000 12/12 375,000 11% 41,250
1,187,500 117,500
Capitalization rate = Total interest / Weighted average loan x 100
=117,500 / 1,187,500 x 100
Capitalization rate = 9.8947%
(W-2) Total borrowing cost to be capitalized.
Expenditure Incurred on Rate Period Capitalization
300,000 May 31, 2003 9.8947% 7/12 17,316
200,000 July 31, 2003 9.8947% 5/12 8,246
500,000 25,562





2 Comments
Qualitative Information & good Effort
ReplyDeleteQualitative Information & good Effort
ReplyDeletePlease do not enter any spam link in the comment box.